Definitions that you should know
When I started learning Azure being a webdev and software architect background. I came across many IT lingo, jargons, abbrebiations that I did know about them. In this post I am putting all those in one place. I hope this will help you as well on your Azure Solution Architect journey!
RADIUS
Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) is a networking protocol that provides centralized authentication, authorization, and accounting management for users who connect and use a network service. RADIUS was developed by Livingston Enterprises in 1991 as an access server authentication and accounting protocol.
EAPOL
Extensible Authentication Access Protocol over LAN
MAC
Media Access Control Address: It uniquely identifies the device in the network. 48-bit hexadecimal number that is hard-coded on a NIC.
ROI
Return on Investment
ISV
independent software vendor
SAN
SAN: storage area network (SAN) By default, Azure VMs are assigned drive D to use as temporary storage
- This drive assignment causes all other attached storage drive assignments to increment by one letter.
- For example, if your on-premises installation uses a data disk that is assigned to drive D for application installations, the assignment for this drive increments to drive E after you migrate the VM to Azure.
- To prevent this automatic assignment, and to ensure that Azure assigns the next free drive letter to its temporary volume, set the storage area network (SAN) policy to OnlineAll:
ARR
Application Request Routing (ARR) is a feature where when a client (or browser) request to any Azure based website, a cookie will be created and stick to the first time request received web site instance.
PIP
A virtual machine running in Azure can now be associated with a direct and publicly accessible IP address that sticks to the VM for its lifetime.
NSG
A network security group (NSG) contains a list of security rules that allow or deny network traffic to resources connected to Azure Virtual Networks (VNet). NSGs can be associated to subnets or individual network interfaces (NIC) attached to VMs.
NIC
A Network Interface (NIC) enables an Azure Virtual Machine to communicate with internet, Azure, and on-premises resources. When creating a virtual machine using the Azure portal, the portal creates one network interface with default settings for you.
RBAC
Role-based access control (RBAC) is a policy-neutral access-control mechanism defined around roles and privileges. The components of RBAC such as role-permissions, user-role and role-role relationships make it simple to perform user assignments.
CMDB
Configuration Management Database
Rack
A Rack has servers (Virtual Machines) in a data-center.
SKU
Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) Learn more about SKU types in Azure
HPC
BeeGFS
(formerly FhGFS) is a parallel file system, developed and optimized for high-performance computing.

PBS
Portable Batch System (or simply PBS) is the name of computer software that performs job scheduling.
SPARK
Apache Spark is a fast and general engine for large-scale data processing. It has a Scala, Java, and Python API and can be run either on either a single node or multi-node configuration. For both cases, it is recommended to have exclusive access of the node in Slurm.
SLURM
Simple Linux Utility for Resource Management (SLURM) is a free and open-source job scheduler for Linux and Unix-like kernels, used by many of the world’s supercomputers and computer clusters.
In order to run an application using a spark context it is first necessary to run a Slurm job which starts a master and some workers.
VPN
Virtual Private Network (VPN). In Azure VPN is a type of Virtual Network Gateway.
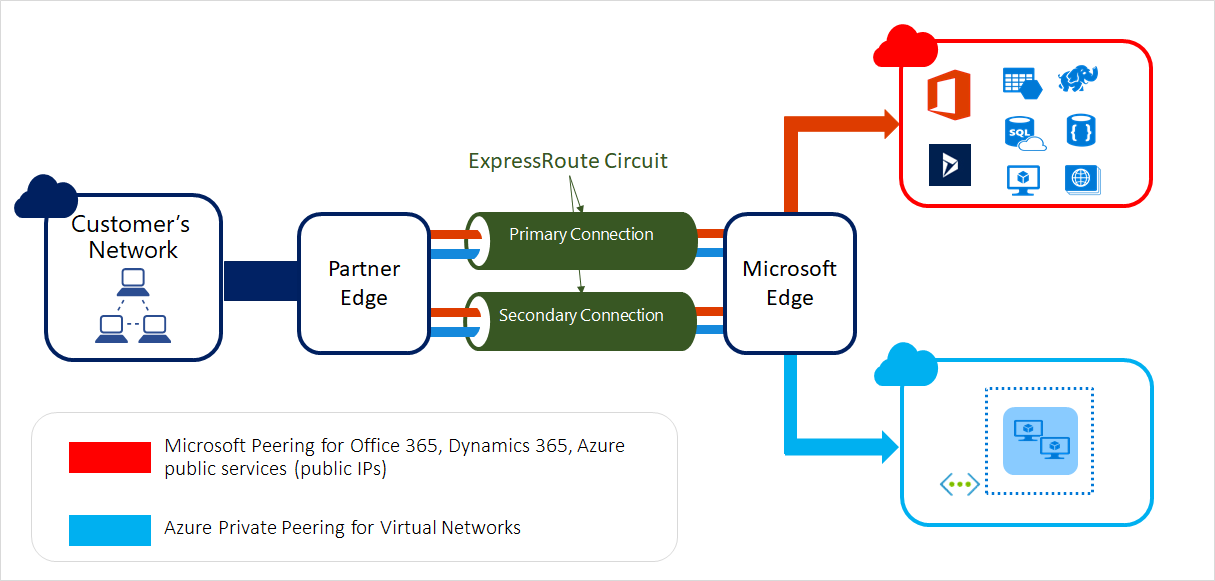
ER
ExpressRoute (ER) lets you extend your on-premises network into the Microsoft cloud over a private connection with the help of connectivity provider.
DMZ
A demilitarized zone (DMZ) is a perimeter network that protects an organization’s internal local-area network (LAN) from untrusted traffic.
VIP
Virtual IP address aka front-end. VIP is an IP address that doesn’t correspond to an actual physical network interface.
DIP
A dynamic IP (DIP) pool is a range of IP addresses.
BGP
“Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)” is a standardized exterior gateway protocol designed to exchange routing and reachability information between autonomous systems (AS) on the Internet.

LSN
Local Site Network (LSN)
IKE
Internet Key Exchange
LNG
The Local Network Gateway (LNG) typically refers to your on-premises location. Learn…
CIDR
Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR). It is an IP address assigning method that improves the efficiency of address distribution. It is also known as supernetting that replaces the older system based on classes A, B, and C networks. By using a single CIDR IP address many unique IP addresses can be designated.
NFS
Network File System (NFS)
VMFS
Virtual Machine File System (VMFS)
SMB
Server Message Block (SMB)

SFTP
Secure File Transfer Protocol
FQDN
Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN)
DMS
Azure Database Migration Service
Cassandra
Apache Cassandra is a free and open-source, distributed, wide-column store, NoSQL database management system designed to handle large amounts of data across many commodity servers, providing high availability with no single point of failure.
Gremlin
Gremlin is a graph traversal language and virtual machine developed by Apache TinkerPop of the Apache Software Foundation. Gremlin works for both OLTP-based graph databases as well as OLAP-based graph processors.
CSP
Cloud Service Provider (CSP)
CSO
Cloud Service Offering (CSO)
CSR
Certificate Signing Request
DISA
Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) is a U.S combat support agency that connects the U.S military and government though IT and communications support. Originally known as the defense communications industry (DCA), the agency was created in 1960, partially in response to communication issues during WWII.
CC SRG
Cloud Computing Security Requirement Guide
FedRAMP
The Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP) provides a standardized approach to security authorizations for Cloud Service Offerings. The Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP) was established in 2011 to provide a cost-effective, risk-based approach for the adoption and use of cloud services by the federal government. FedRAMP empowers agencies to use modern cloud technologies, with an emphasis on security and protection of federal information.
https://www.fedramp.gov/program-basics/
FedRAMP Plus
FedRAMP+ is the concept of leveraging the work done as part of the FedRAMP assessment, and adding specific security controls and requirements necessary to meet and assure DoD’s critical mission requirements. A CSP’s CSO can be assessed in accordance with the criteria outlined in this SRG, with the results used as the basis for awarding a DoD provisional authorization.
DoD
The Department of Defense (DoD) is responsible for providing the military forces needed to deter war and protect the security of our country. The major elements of these forces are the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, and Air Force, consisting of about 1.3 million men and women on active duty.
NIST
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is a non-regulatory government agency that develops technology, metrics, and standards to drive innovation and economic competitiveness at U.S.-based organizations in the science and technology industry.
CA
Certificate Authority (CA) like Entrust, Thwate, Verisign
DNS
Domain Name System (DNS) is the phonebook of the Internet.
UDR
User Defined Routing (UDR)
NAT
Network Address Translation (NAT)
SSH
Secure Shell (SSH) protocol used to communicate machines. It encrypts the data while sending data to other machine. It works on applciation layer (layer-7) of OSI model.
Telnet
Teletype Network (Telnet) developed in 1969. Plain text communication between machines. Good for LAN since data in not encrypted. Not good for sensitive data. It works on applciation layer (layer-7) of OSI model.
SNAT
Source Network Address Translation (SNAT) allows traffic from a private network to go out to the internet. Virtual machines launched on a private network can get to the internet by going through a gateway capable of performing SNAT. The device performing NAT changes the private IP address of the source host to public IP address.

DNAT
Destination Network Address Translation (DNAT) : Destination NAT changes the destination address in the IP header of a packet.
NVA
Network Virtual Appliances (NVAs): An NVA(Network Virtual Appliance) is typically used to control the flow of network traffic from a perimeter network, also known as a DMZ, to other networks or subnets.
ILB
Internal Load Balancer(ILB) is a security enhancement over the current public load balancing that is offered in Azure.
HA Ports
High Available Ports: High availability (HA) ports is a type of load balancing rule that provides an easy way to load-balance all flows that arrive on all ports of an internal Standard Load Balancer.
NAS
Network Attached Storage (NAS)
RAID
Redundant Array of Inexpensive/independent Disks(RAID). It was created in 1988 as a means to combat the rising cost of disk drives. You’ll often hear RAID as it relates to network attached storage or “NAS”. You know in movies when you see the “mainframe” and it’s rows and rows of hard drives backing up all of the evil corporation’s information? That’s NAS, and that’s RAID in action. RAID Wikipedia
ALE
Annual Loss Expectancy
ALE = SLE x ARO
SLE
Single Loss Expectancy
ARO
Annualized Rate of Occurrence
CIA
CIA - Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability. The CIA Triad is actually a security model that has been developed to help people think about various parts of IT security.
IPS
Intrusion Prevention System
IDS
Intrusion Detection System
WAF
web application firewall (WAF)
LDAP
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol “Address Book” of user accounts used to authenticate users. Identifies level of acess, group membership etc.
SQL
Structured Query Language(SQL)
FQDNs
fully qualified domain names (FQDNs)
DNAT
Destination Network Address Translation (DNAT)
WAP
Wireless Access Point (WAP)
ICMP
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is one of the protocols of the TCP/IP suite. The ICMP echo request and the ICMP echo reply messages are commonly known as ping messages.
DDoS
Distributed denial of service (DDoS) Learn More. In a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack, an attacker attempts to overwhelm a targeted server or network with junk network traffic — somewhat like bombarding a restaurant with fake delivery orders until it cannot provide service to legitimate customers.
Workgroups
A workgroup is a collection of computers that each maintain their own security information. Here the security is distributed, not centralized.
Domains
A domain is a collection of computers where security is handled centrally.Each domain has one or more domain controllers.
ICMP
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is a control protocol, meaning that it designed to not carry application data, but rather information about the status of the network itself. The best known example of ICMP in practice is the ping utility, that uses ICMP to probe remote hosts for responsiveness and overall round-trip time of the probe messages.
URL
Universal Resource Locator (URL)
OSI Layers
Open System Interconnection (OSI)
- Software Layer
- Application Layer
- Presentation Layer
- Session Layer
- Heart of OSI
- Transport Layer
- Hardware Layer
- Network Layer
- Data Link Layer
- Physical Layer
🏆 Pro Tip
Top Down: All People Seems To Need Data Processing.
Bottom Up: Please Do Not Through Sausage Pizza Away.
Protocol
In networking, a protocol is a specified way of formatting data so that any networked computer can interpret the data.
Protocols and their ports:
- HTTP = 80
- FTP = 21 and 22
- SMTP = 58
- SMTP = 25
- DNS = 53
- SSL = 443
UDP
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is a connection-less transportation protocol. UDP is used to pass the actual user data. Communication is datagram oriented, so the integrity is guaranteed only on the single datagram. Datagrams reach destination and can arrive out of order or don’t arrive at all. It’s generally used for real time communication, where a little percentage of packet loss rate is preferable to the overhead of a TCP connection. It is an Transport layer (layer-4) protocol. UDP, the User Datagram Protocol, does not set up these dedicated connections.
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) TCP is a connection oriented transportation protocol. TCP is used to pass the actual user data. It guarantees that all sent packets will reach the destination in the correct order. TCP, the Transmission Control Protocol, sets up dedicated connections between devices and ensures that all packets arrive.
SSL
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) now it is deprecated. It is session layer protocol. It is presentation and session layer protocol. It lies between Transport and application layer.

TLS
Transport Layer Security (TLS) provides communications security over a computer network. It is presentation and session layer protocol. It lies between Transport and application layer.

IP
Internet Protocol (IP)
IPSec
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec): IPsec is a group of protocols that are used together to set up encrypted connections between devices. IPsec is often used to set up VPNs, and it works by encrypting IP packets, along with authenticating the source where the packets come from. IPsec uses UDP because this allows IPsec packets to get through firewalls.
IPsec is not one protocol, but a suite of protocols. Internet Protocol (IP) is not part of the IPsec suite, IPsec runs directly on top of IP. The following protocols make up the IPsec suite:
Authentication Header (AH): The AH protocol ensures that data packets are from a trusted source and that the data has not been tampered with, like a tamper-proof seal on a consumer product. These headers do not provide any encryption; they do not help conceal the data from attackers.
Encapsulating Security Protocol (ESP): ESP encrypts the IP header and the payload for each packet — unless transport mode is used, in which case it only encrypts the payload. ESP adds its own header and a trailer to each data packet.
Security Association (SA): SA refers to a number of protocols used for negotiating encryption keys and algorithms. One of the most common SA protocols is Internet Key Exchange (IKE).
Reference: https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/network-layer/what-is-ipsec/
Packet
All data sent over a network is broken up into smaller pieces called packets, and all packets have two parts: the payload and the header. The payload is the packet’s actual contents, the data being sent. The header has information about where the packet comes from and what group of packets it belongs to. Each network protocol attaches a header to each packet.
Tunelling
Encapsulating packets within other packets is called “tunneling”.
To understand why this is called “tunneling,” we can change the analogy slightly. If a car needs to pass from Point A on one side of a mountain to Point B on the other side, the most efficient way is to simply go through the mountain. However, ordinary cars are not capable of going straight through solid rock. As a result, the car has to drive all the way around the mountain to get from Point A to Point B.
But imagine that a tunnel was created through the mountain. Now, the car can drive straight from Point A to Point B, which is much faster, and which it could not do without the tunnel.
GRE
Generic Routing Encapsulation, or GRE, is a protocol for encapsulating data packets that use one routing protocol inside the packets of another protocol. “Encapsulating” means wrapping one data packet within another data packet, like putting a box inside another box. To understand how this works, think about the difference between a car and a ferry. A car travels over roads on land, while a ferry travels over water. A car cannot normally travel on water — however, a car can be loaded onto a ferry in order to do so.
Reference: https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/network-layer/what-is-gre-tunneling/
IPV
Internet Protocol Version (IPV). IPv6 is more advanced and has better features compared to IPv4.
NTP
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a networking protocol for clock synchronization between computer systems over packet-switched, variable-latency data networks.
TDS
The Tabular Data Stream (TDS) Protocol is an application-level protocol used for the transfer of requests and responses between clients and database server systems. a TDS session is established when the transport-level connection is established and the server receives a request to establish a TDS connection. It persists until the transport-level connection is terminated (for example, when a TCP socket is closed).

OLTP
OLTP (Online Transactional Processing)
SMTP
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) to send emails.
DDL
Data Definition Language (DDL)
K-ISMS
Korea-Information Security Management System (K-ISMS)
B2C
Business-To-Consumer (B2C)
ISV
Independent Software Vendor (ISV) - also known as a software publisher, is an organization specializing in making and selling software, as opposed to computer hardware, designed for mass or niche markets.
LOB
line-of-business (LOB) - used only for your company or your employees.
ITSM
IT Service Management (ITSM) Few ITSM tools are ServiceNow, System Center Service Manager, Provance, Cherwell. You can use IT Service Management Connector in Azure to connect your own ITSM tools.
SIEM
Security Incident and Event Monitoring (SIEM) - Microsoft Azure Sentinel is a scalable, cloud-native, security information event management (SIEM) and security orchestration automated response (SOAR) solution.
VNet
Virtual Network: This is Private network on Azure Cloud.
VPC
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) this is similar to VNet in Azure.
EC2
Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) Instance: This is a Virtual Machine on Amazon.
UPN
user principal name (UPN)
SPN
security principal name (SPN)
MSAL
Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL)
ADAL
Active Directory Authentication Library (ADAL)
Active Directory Authentication Library (ADAL) integrates with the Azure AD for developers (v1.0) endpoint, where MSAL integrates with the Microsoft identity platform. Learn More…
OIDC
OpenID Connect (OIDC) - authentication and authorization protocol
MSRP
Managed Identity Resource Provider (MSRP)
ATP
Azure Advanced Threat Protection ( ATP ) - Now it is known as “Microsoft Defender for Identity”
SSPR
Self-Service Password Reset
SSPI
Security Support Provider Interface (SSPI) is a component of Windows API that performs a security-related operations such as authentication.
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) : related to IP Addressing.
DHCP helps ensure that devices ultimately correctly configured to join networks. DHCP does this by assigning IP addresses and other information to each host (or device) connecting to a network.
Delta Query
Delta query enables applications to discover newly created, updated, or deleted entities without performing a full read of the target resource with every request.
Workbook Playbook Notebook Runbook
- Workbook : Visualize data by Kusto query. Azure Workbooks is a great tool for operations and
DevOpsteams because they can combine metrics and queries. - Playbook: Playbooks are collections of procedures that can be run from Azure Sentinel in response to an alert or incident.
- Notebook: Azure Notebooks is an implementation of the widely used open-source
Jupyter Notebook. - Runbooks: are used to create automation in Azure. Like in the evening shut down all of the DEV Virtual machines.
Front Door vs Traffic Manager
| FrontDoor | Traffic Manager |
|---|---|
| Http and Https protocol | Used for File and Image |
| Used for multi region app, agnostic of PIP public IP | Used for sharing and accessing multi-region deployed Files and Images, agnostic of PIP public IP |
How many VNets allowed in Azure?
500 VNets, You can only have one VPN Gateway with 1 VNet.




